What is the cloud?
You may have heard people using terms like the cloud, cloud computing, or cloud storage. But what exactly is the cloud?
Simply put, the cloud is the Internet—more specifically, it's all of the things you can access remotely over the Internet. When something is in the cloud, it means it's stored on Internet servers instead of your computer's hard drive.
Why use the cloud?
Some of the main reasons to use the cloud are convenience and reliability. For example, if you've ever used a web-based email service, such as Gmail or Yahoo! Mail, you've already used the cloud. All of the emails in a web-based service are stored on servers rather than on your computer's hard drive. This means you can access your email from any computer with an Internet connection. It also means you'll be able to recover your emails if something happens to your computer.
Uses of cloud computing
You’re probably using cloud computing right now, even if you don’t realize it. If you use an online service to send emails, edit documents, watch movies or TV, listen to music, play games, or store pictures and other files, cloud computing is likely making it all possible behind the scenes. A variety of organizations—from tiny startups to global corporations, government agencies to non-profits—have embraced cloud computing technology for all sorts of reasons.
Here are a few examples of what’s possible with cloud services from a cloud provider:
Create cloud-native applications
Quickly build, deploy, and scale applications—web, mobile, and API. Take advantage of cloud-native[RM1] technologies and approaches, such as containers, Kubernetes, microservices architecture, API-driven communication, and DevOps.
Store, back up, and recover data
Protect your data more cost-efficiently—and at a massive scale—by transferring your data over the internet to an offsite cloud storage system that’s accessible from any location and any device.
Stream audio and video
Connect with your audience anywhere, anytime, on any device with high-definition video and audio with global distribution.
Deliver software on demand
Also known as software as a service (SaaS), on-demand software lets you offer the latest software versions and updates to customers—anytime they need, anywhere they are.
Test and build applications
Reduce application development costs and time by using cloud infrastructures that can easily be scaled up or down.
Analyze data
Unify your data across teams, divisions, and locations in the cloud. Then use cloud services, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to uncover insights for more informed decisions.
Embed intelligence
Use intelligent models to help engage customers and provide valuable insights from the data captured.
Type of cloud:
Public Cloud
Private Cloud
Hybrid Cloud
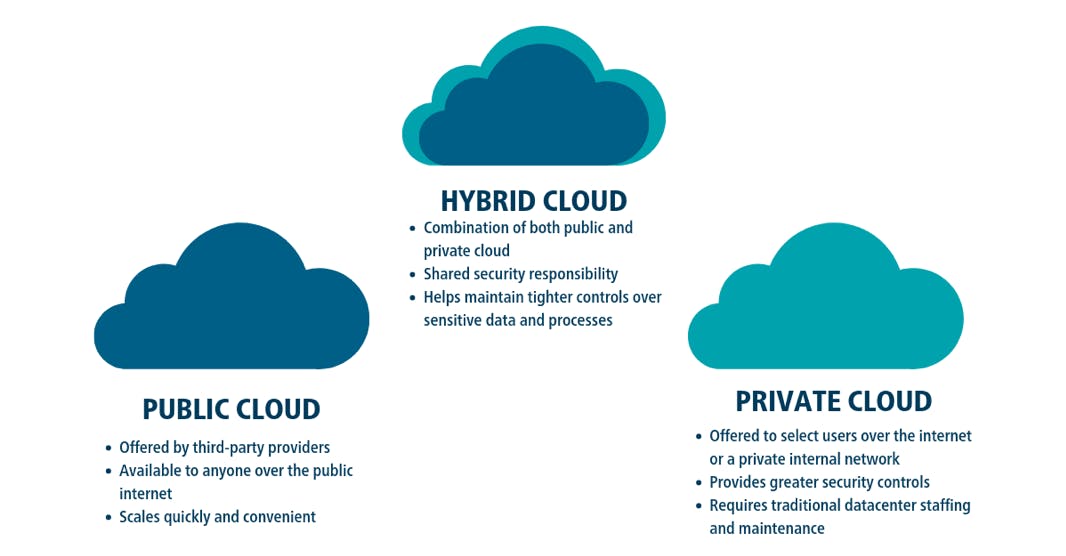
Public Cloud:
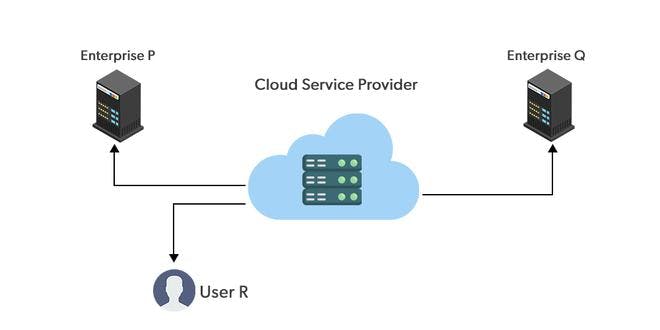
Computing in which service provider makes all resources public over the internet. It is connected to the public Internet. Service provider serves resources such as virtual machines, applications, storage, etc to the general public over the Internet. It may be free of cost or with minimal pay-per-usage. It is available for public display, Google uses the cloud to run some of its applications like Google Docs, Google Drive YouTube, etc.
It is the most common way of implementing cloud computing. The external cloud service provider owns, operates, and delivers it over the public network.
It is best for companies that need an infrastructure to accommodate a large number of customers and work on projects that have diverse organizations i.e. research institutions and NGOs etc.
Public Cloud Advantages:
Scalability: Public cloud services are designed to be scalable, which means you can easily add or remove resources as needed.
Cost-Effective: Public cloud providers typically offer a pay-as-you-go model, which allows you to only pay for the resources you use, making it cost-effective.
Accessibility: Public cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, which makes it easy to access data and applications from anywhere in the world.
Reliability: Public cloud providers usually have multiple data centres across different locations, which ensures high availability and reliability.
Public Cloud Disadvantages:
Security: Since public cloud services are available to anyone with an internet connection, there is a risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
Control: Public cloud providers have control over the infrastructure and services, which means you have limited control over how your data is stored and managed.
Compliance: Compliance requirements can be a challenge for public cloud users since they have to comply with the regulations and standards that apply to the cloud provider.
Private Cloud:
Computing in which the service provider does not make all resources public over the internet. It only supports connectivity over the private network. It has only authentic users and single-occupant architecture. Google back-end data of applications like Google Drive, Google Docs, YouTube, etc are not available to the public, these types of data and applications run on a private cloud.
The infrastructure and services are maintained and deployed over a private network; hardware and software are dedicated only to a private company i.e. members of the special entity.
It is best for companies that need an infrastructure that has high performance, high security, and privacy due to its adaptability and flexibility.
Private Cloud Advantages:
Control: Private cloud users have full control over the infrastructure and services, which means they can customize the environment to their specific needs.
Security: Private cloud services are typically more secure since they are only accessible to authorized users.
Compliance: Private cloud users have more control over compliance requirements since they can customize the environment to meet specific regulatory requirements.
Customization: Private cloud users can customize the environment to their specific needs, which means they can optimize performance and efficiency.
Private Cloud Disadvantages:
Cost: Private cloud services can be more expensive than public cloud services since they require a dedicated infrastructure.
Maintenance: Private cloud users are responsible for maintaining and updating the infrastructure, which can be time-consuming and costly.
Scalability: Private cloud services can be less scalable than public cloud services, which means they may not be able to handle sudden spikes in demand.
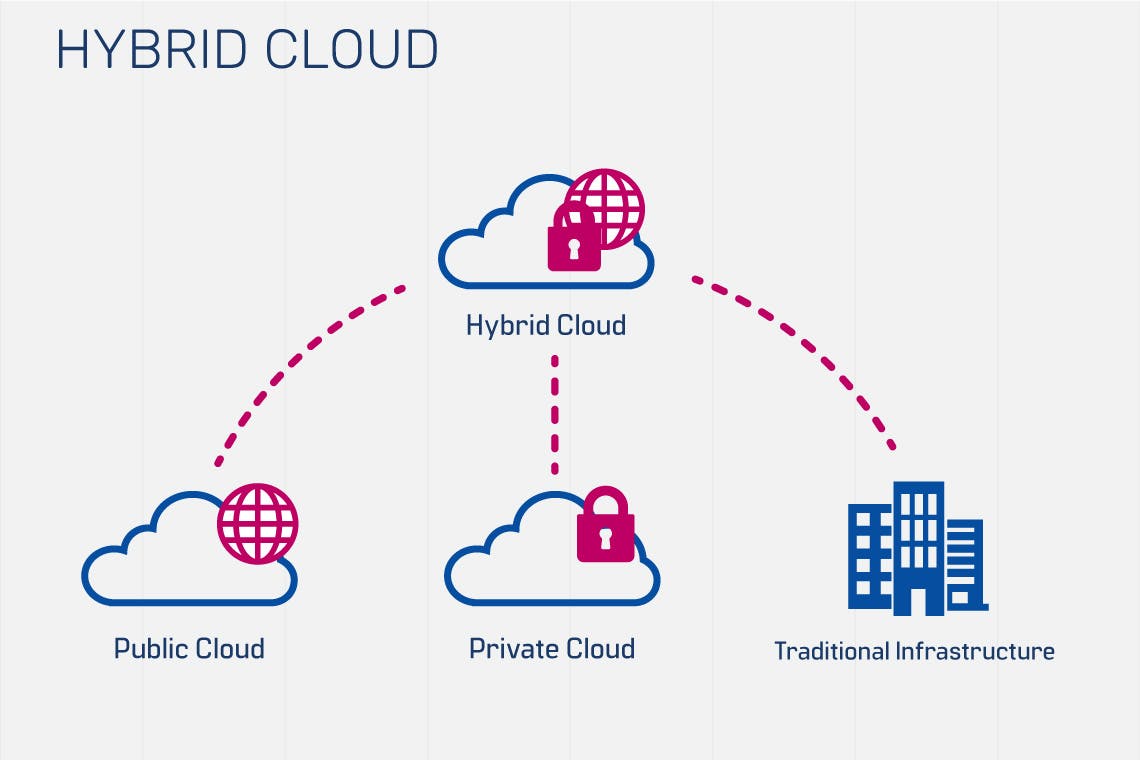
Hybrid Cloud:
A hybrid cloud is a mixed computing environment where applications are run using a combination of computing, storage, and services in different environments—public clouds and private clouds, including on-premises data centres or “edge” locations. Hybrid cloud computing approaches are widespread because almost no one today relies entirely on a single public cloud.
Hybrid cloud solutions enable you to migrate and manage workloads between these various cloud environments, allowing you to create more versatile setups based on your specific business needs. Many organizations choose to adopt hybrid cloud platforms to reduce costs, minimize risk, and extend their existing capabilities to support digital transformation efforts.
Hybrid Cloud Advantages:
Flexible and Secure: It provides flexible resources because of the public cloud and secure resources because of the private cloud.
Cost: It offers the features of both the public as well as the private cloud. A hybrid cloud is capable of adapting to the demands that each company needs for space, memory, and systems.
Security: A hybrid cloud is secure because critical activities are performed by the private cloud.
Risk Management: A hybrid cloud provides an excellent way for companies to manage risk.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud
Network Issues: In the Hybrid Cloud, networking becomes complex because of the private and the public cloud.
Infrastructure Compatibility: Infrastructure compatibility is the major issue in a hybrid cloud. With dual levels of infrastructure, a private cloud controls the company, and a public cloud does not, so there is a possibility that they are running in separate stacks.
Reliability: The reliability of the services depends on cloud service providers.

