✨ What is Linux?
- Linux is an open-source operating system modelled on UNIX. It's the foundation
of many cloud infrastructures and has a significant presence in the server world, among other places.
✨ Basic Fundamentals of Linux:
- Kernel: It's the core component of the system that interacts with hardware.
- Shell: An interface that allows users to interact with the kernel using command lines or scripts.
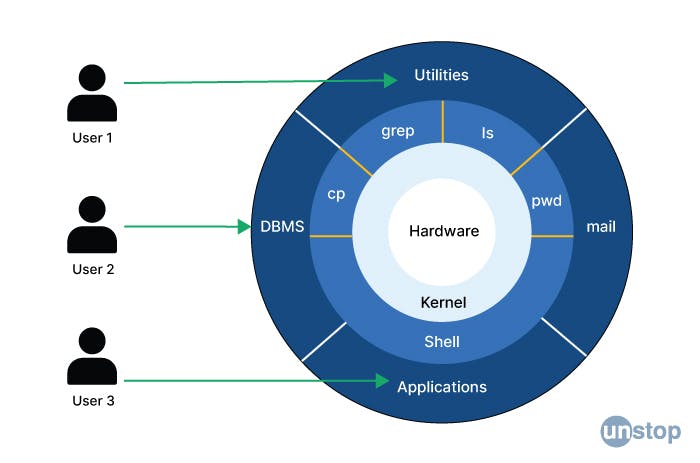
- File System: Hierarchical structure where all the data is organized.
**Note: Comprehensive Insight into the Linux File System
- Processes: Running instances of programs. Linux treats almost everything as a process.
- User & Groups: Security and permissions are based on users and groups.
✨ The Command Line Interface (CLI)
One of the defining features of Linux is the command line interface or CLI. Unlike graphical user interfaces (GUIs), the CLI requires users to type commands to interact with the system. This might seem intimidating at first, but it offers significant advantages, such as greater control and efficiency.
Common Linux CLI commands:
ls: List files and directories.cd: Change the current directory.mkdir: Create a new directory.touch: Create a new file.cp: Copy files or directories.mv: Move or rename files or directories.rm: Remove files or directories.pwd: Print the current working directory.
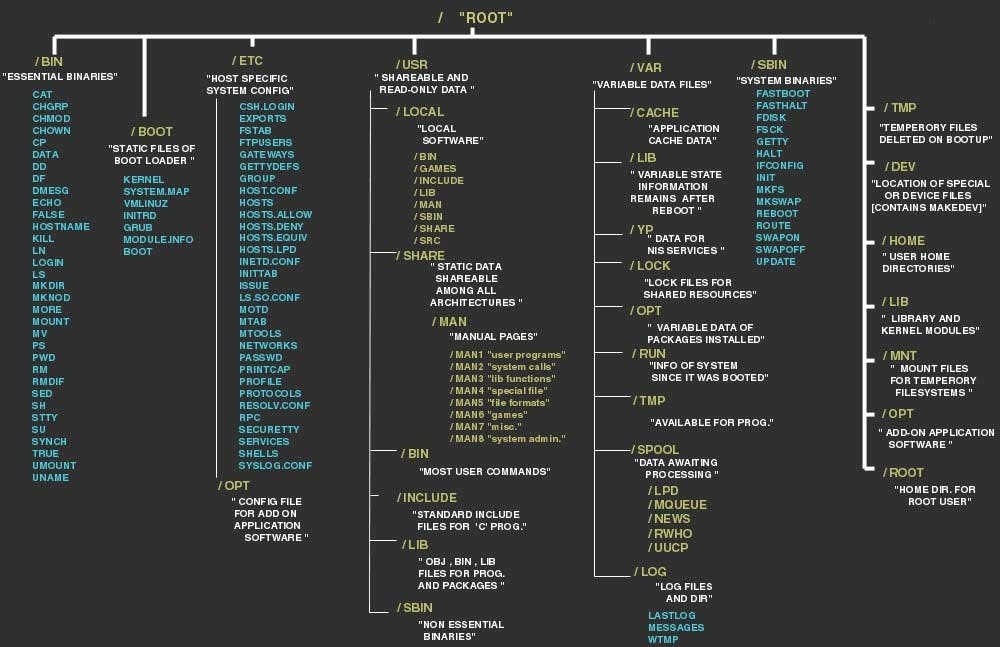
✨ File System Hierarchy
Linux organizes files and directories in a hierarchical structure. The root directory is denoted by /, and all other directories and files branch out from there. Understanding this hierarchy is crucial for navigation and proper file management.
Common directories include:
/bin: Essential system binaries./etc: Configuration files./home: User home directories./usr: User-installed software./var: Variable data (e.g., logs)./tmp: Temporary files./dev: Device files.
✨ Users and Permissions
Linux is known for its robust user and permission management system. Each user has a unique username and belongs to one or more groups. File permissions are specified using a combination of read (r), write (w), and execute (x) permissions for the owner, group, and others.
The chmod command is used to change file permissions, while chown is used to change file ownership. Understanding and managing these permissions is crucial for securing your system.
✨ Package Management
Linux distributions come with package management systems that make it easy to install, update, and remove software. For instance, Ubuntu uses apt, while CentOS uses yum. These tools fetch software from online repositories, ensuring that you always have access to the latest updates and security patches.
To install a package, you typically use a command like:
sudo apt-get install package_name
✨ Update and Upgrade
Regular system updates and upgrades are essential to keep your Linux system secure and up-to-date. Use the following commands to perform these tasks:
sudo apt-get update: Update the package lists.sudo apt-get upgrade: Upgrade installed packages.
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade: Upgrade the distribution.
✨ System Information
You can retrieve important system information using various commands, such as:
uname -a: Display system information.df -h: Show disk usage.free -h: Display memory usage.toporhtop: Monitor system processes.
Linux Commands You Must Know as a Regular User
ls - The most frequently used command in Linux to list directories
pwd - Print working directory command in Linux
cd - Linux command to navigate through directories
mkdir - Command used to create directories in Linux
mv - Move or rename files in Linux
cp - Similar usage as mv but for copying files in Linux
rm - Delete files or directories
touch - Create blank/empty files
ln - Create symbolic links (shortcuts) to other files
cat - Display file contents on the terminal
clear - Clear the terminal display
echo - Print any text that follows the command
less - Linux command to display paged outputs in the terminal
man - Access manual pages for all Linux commands
uname - Linux command to get basic information about the OS
whoami - Get the active username
tar - Command to extract and compress files in Linux
grep - Search for a string within an output
head - Return the specified number of lines from the top
tail - Return the specified number of lines from the bottom
diff - Find the difference between two files
cmp - Allows you to check if two files are identical
comm - Combines the functionality of diff and cmp
sort - Linux command to sort the content of a file while outputting
export - Export environment variables in Linux
zip - Zip files in Linux
unzip - Unzip files in Linux
ssh - Secure Shell command in Linux
service - Linux command to start and stop services
ps - Display active processes
kill and killall - Kill active processes by process ID or name
df - Display disk filesystem information
mount - Mount file systems in Linux
chmod - Command to change file permissions
chown - Command for granting ownership of files or folders
ifconfig - Display network interfaces and IP addresses
traceroute - Trace all the network hops to reach the destination
wget - Direct download files from the internet
ufw - Firewall command
iptables - Base firewall for all other firewall utilities to interface with
apt, pacman, yum, rpm - Package managers depending on the distro
sudo - Command to escalate privileges in Linux
cal - View a command-line calendar
alias - Create custom shortcuts for your regularly used commands
dd - Majorly used for creating bootable USB sticks
whereis - Locate the binary, source, and manual pages for a command
whatis - Find what a command is used for
top - View active processes live with their system usage
useradd and usermod - Add new user or change existing users data
passwd - Create or update passwords for existing users

