In the vast landscape of cloud computing, security and access control stand as paramount pillars. Amazon Web Services (AWS), a leading cloud services provider, places a significant emphasis on ensuring the utmost security for its users. One of the cornerstones of security within AWS is the Identity and Access Management (IAM) service.
What is AWS IAM?
AWS IAM is a powerful service that enables control and management of access to AWS services and resources securely. Think of it as the gatekeeper of your AWS kingdom, allowing you to manage users, permissions, and access to AWS services and resources with precision.
Key Components of AWS IAM:
1. Users
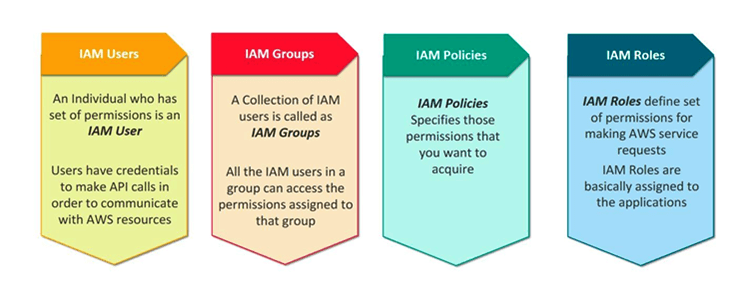
IAM allows the creation of individual users, each with unique security credentials (such as access keys, passwords, and multi-factor authentication devices) and permissions to access AWS resources.
2. Groups
Users with similar permissions can be grouped together for easier management. Groups help in assigning permissions to multiple users at once, simplifying the access control process.
3. Roles
IAM roles define a set of permissions for making AWS service requests. Roles are not associated with a specific user or group but can be assumed by users, applications, or AWS services when needed.
4. Policies
Policies in IAM are JSON documents that define permissions. These policies are attached to users, groups, or roles, outlining what actions are allowed or denied on which AWS resources.
5. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
IAM supports multi-factor authentication, adding an extra layer of security by requiring users to present two or more pieces of evidence (factors) when logging in or performing sensitive actions.
Benefits of AWS IAM:
1. Enhanced Security
IAM allows fine-grained control over who can access AWS resources and how they can access them, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive data.
2. Granular Access Control
By using IAM, permissions can be tailored precisely to match specific roles or responsibilities within an organization, ensuring users have access only to the resources they need.
3. Centralized Management
IAM provides a centralized location to manage users, groups, roles, and their respective permissions, making it easier to enforce security policies across an organization.
4. Compliance and Auditing
IAM enables tracking and auditing of user activity and access to AWS resources, helping organizations meet compliance requirements and investigate security incidents.
Best Practices for AWS IAM:
Principle of Least Privilege: Grant only the permissions necessary for users, groups, or roles to perform their tasks.
Regularly Review Permissions: Continuously monitor and review IAM policies to ensure they align with the current security requirements.
Enable MFA: Enforce multi-factor authentication for an added layer of security.
Use IAM Roles for AWS Resources: Assign roles to AWS resources to avoid hardcoding credentials and enhance security.
Utilize IAM Policy Conditions: Define conditions within policies to add flexibility and control over access.
In a nutshell, AWS IAM is your superhero when it comes to guarding your cloud kingdom. By following its lead and using its awesome powers wisely, you can keep your digital world safe, secure, and running smoothly.

