In the rapidly evolving world of software development, automation is key to maintaining efficiency and ensuring the quality of software products. Enter Jenkins, an open-source continuous integration and continuous delivery/deployment (CI/CD) automation server that has become an essential tool in the DevOps toolkit. Written in Java, Jenkins enables developers to automate the building, testing, and deploying of software, streamlining the entire development lifecycle.
What is Jenkins?
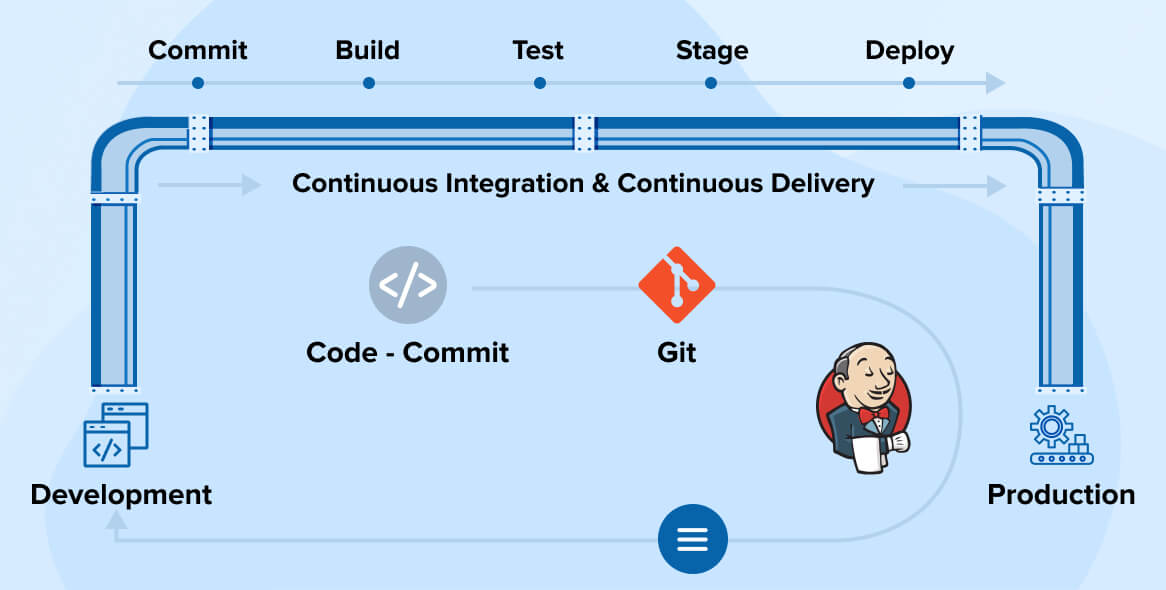
Jenkins is an open-source automation server designed to facilitate continuous integration and continuous delivery/deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. As a Java-based application, Jenkins provides a robust platform for managing various stages of the software development process, from code integration to deployment.
With Jenkins, developers can automate repetitive tasks, thereby reducing manual intervention and minimizing the risk of errors. By automating the integration of code changes, Jenkins ensures that new code is regularly built, tested, and integrated into the main codebase, making it easier to detect and fix bugs early in the development cycle.
Why Jenkins?
In today's fast-paced development environment, automation is no longer a luxury—it's a necessity. Developers often juggle multiple tasks, and manual processes can lead to inefficiencies and errors. Jenkins addresses these challenges by providing a platform that automates the end-to-end development workflow.
Here's why Jenkins is indispensable:
Efficiency: Automation reduces the time and effort required to manually build, test, and deploy software.
Consistency: Automated processes ensure that tasks are performed the same way every time, reducing variability and errors.
Early Bug Detection: Continuous integration allows for early detection of integration issues, making it easier to address bugs before they become significant problems.
Scalability: Jenkins supports distributed builds, allowing for the scaling of operations across multiple machines.
Extensibility: With its extensive plugin ecosystem, Jenkins can integrate with various tools and platforms, making it adaptable to various development environments.
Key Features of Jenkins
Pipeline as Code: Define your build, test, and deployment pipelines as code, ensuring they are version-controlled and easily maintainable.
Extensive Plugin Ecosystem: Jenkins supports various plugins, enabling integration with various DevOps tools such as Git, Maven, Docker, and AWS.
Community and Support: As an open-source tool, Jenkins benefits from a large and active community that contributes to its development and provides support through forums and documentation.
Getting Started with Jenkins
Before diving into the procedural aspects of Jenkins, it's essential to understand its necessity in modern development workflows. Jenkins automates the integration and deployment of code, eliminating the need for manual oversight of individual processes. By streamlining these workflows, Jenkins allows developers to focus on what they do best—writing code.
Note: Ensure Jenkins is installed on your machine. If not, follow the installation guide to set it up.
Task 2: Create a Freestyle Pipeline to Print "Hello World"
Let's walk through creating a Freestyle pipeline in Jenkins that accomplishes the following tasks:
Print "Hello World"
Print the Current Date and Time
Clone a GitHub Repository and List Its Contents
Configure the Pipeline to Run Periodically (e.g., every hour)
Step-by-Step Guide:
Create a New Freestyle Project:
Open Jenkins and click on "New Item."
Enter a name for your project and select "Freestyle project."
Click "OK."
Add Build Steps:
On the project configuration page, scroll down to the "Build" section.
Click "Add build step" and select "Execute shell."
Add Shell Commands:
In the shell command box, add the following commands:
echo "Hello World" echo "Current Date and Time: $(date)" git clone https://github.com/rajatchauhan-git/GitLab-Zero-to-Hero.git ls GitLab-Zero-to-HeroThis script will print "Hello World," the current date and time, clone a GitHub repository, and list its contents.
Set Build Triggers:
In the project configuration page, scroll down to the "Build Triggers" section.
Check "Build periodically" and enter the schedule. For example, to run the job every hour, enter
H * * * *.
Save the Project:
- Click "Save" to apply the configuration.
Run the Pipeline:
You can trigger the pipeline manually by clicking "Build Now" on the project page.
The pipeline will also run automatically according to the specified schedule.

Console Output
Started by user rajat chauhan
Running as SYSTEM
Building on the built-in node in workspace /var/lib/jenkins/workspace/Jenkins Task
[Jenkins Task] $ /bin/sh -xe /tmp/jenkins10188657440169460580.sh
+ echo Hello World
Hello World
+ date
+ echo Current Date and Time: Fri Aug 2 21:06:05 UTC 2024
Current Date and Time: Fri Aug 2 21:06:05 UTC 2024
+ git clone https://github.com/rajatchauhan-git/GitLab-Zero-to-Hero.git
Cloning into 'GitLab-Zero-to-Hero'...
+ ls GitLab-Zero-to-Hero
Assets
Day-1
Day-2
Day-3
Day-4
Day-5
README.md
Finished: SUCCESS

